Unlock the Full Potential of Single Cell Sequencing for the First Time
Accurate Somatic SNV Detection in Single Cells Now Possible
AccuSomatic™ Amplification for Single Cell Sequencing enables the discovery of true somatic single nucleotide variations (SNVs) in single cells that could not be accurately detected by any prior methods.
Before scientists can analyze the genome of a single cell, they must first obtain sufficient amounts of its DNA by whole genome amplification (WGA). But WGA typically produces errors that falsely indicate the presence of mutations and obscure the detection of any true somatic mutations. Existing methods, including all commercial kits available today, suffer from multiple sources of artifacts which result in more than 20,000 false somatic SNV calls per cell and >90% false positive results.
AccuSomatic Amplification eliminates >99% of the false positive somatic SNV calls while maintaining the same detection sensitivity. This breakthrough makes it possible, for the first time, to accurately detect the true somatic SNVs at the single cell level. It will greatly expand the capability of researchers to explore the landscapes of somatic mutations in human and other organisms beyond the reach of other amplification techniques available today.
To date, our highly robust system has been successfully applied to >2000 single-cell whole genome sequencing for multiple cell types in human, mouse, and rat. We are providing it as a service to allow global researchers to unlock the full potential of single cell sequencing in cancer, drug development, and aging research.
The AccuSomatic Amplification Breakthrough
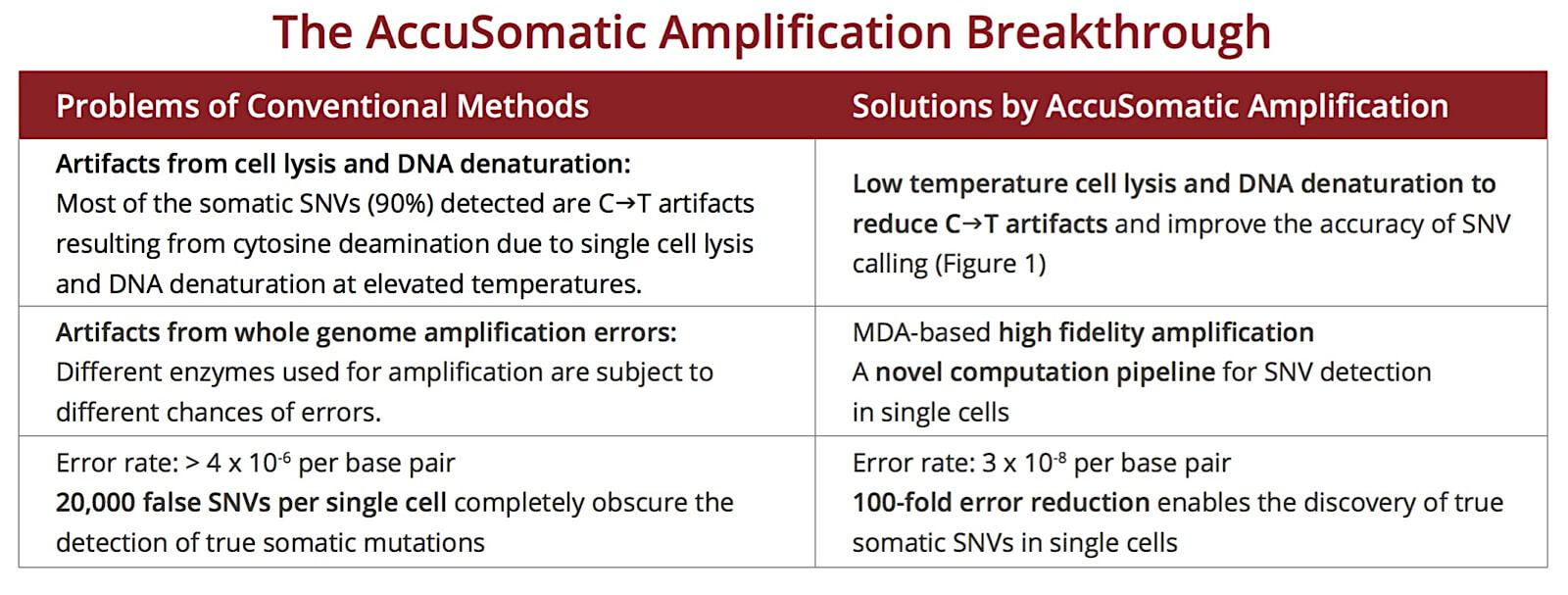
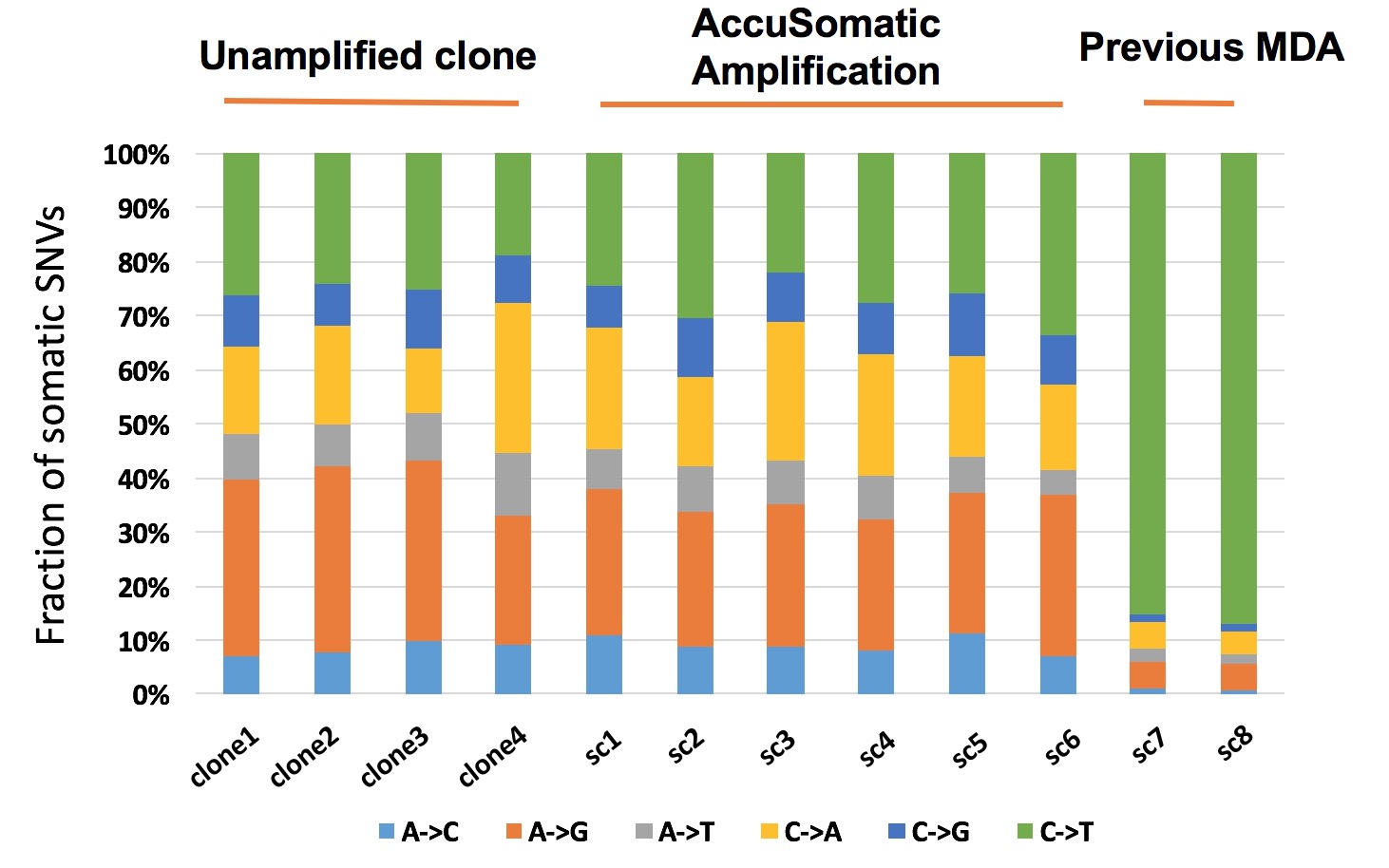
Figure 1. AccuSomatic Amplification eliminates the cytosine deamination artifacts in prior methods.
Single cells undergoing AccuSomatic Amplification have a similar C->T mutation ratio to unamplified clones derived from cells in the same population of human dermal fibroblasts. On the other hand, for single cells treated with conventional high-temperature lysis/DNA denaturation and amplified with a commercially available MDA-based kit, 90% of the somatic SNVs detected are C->T mutations, most of the artifacts caused by cytosine deamination [1].
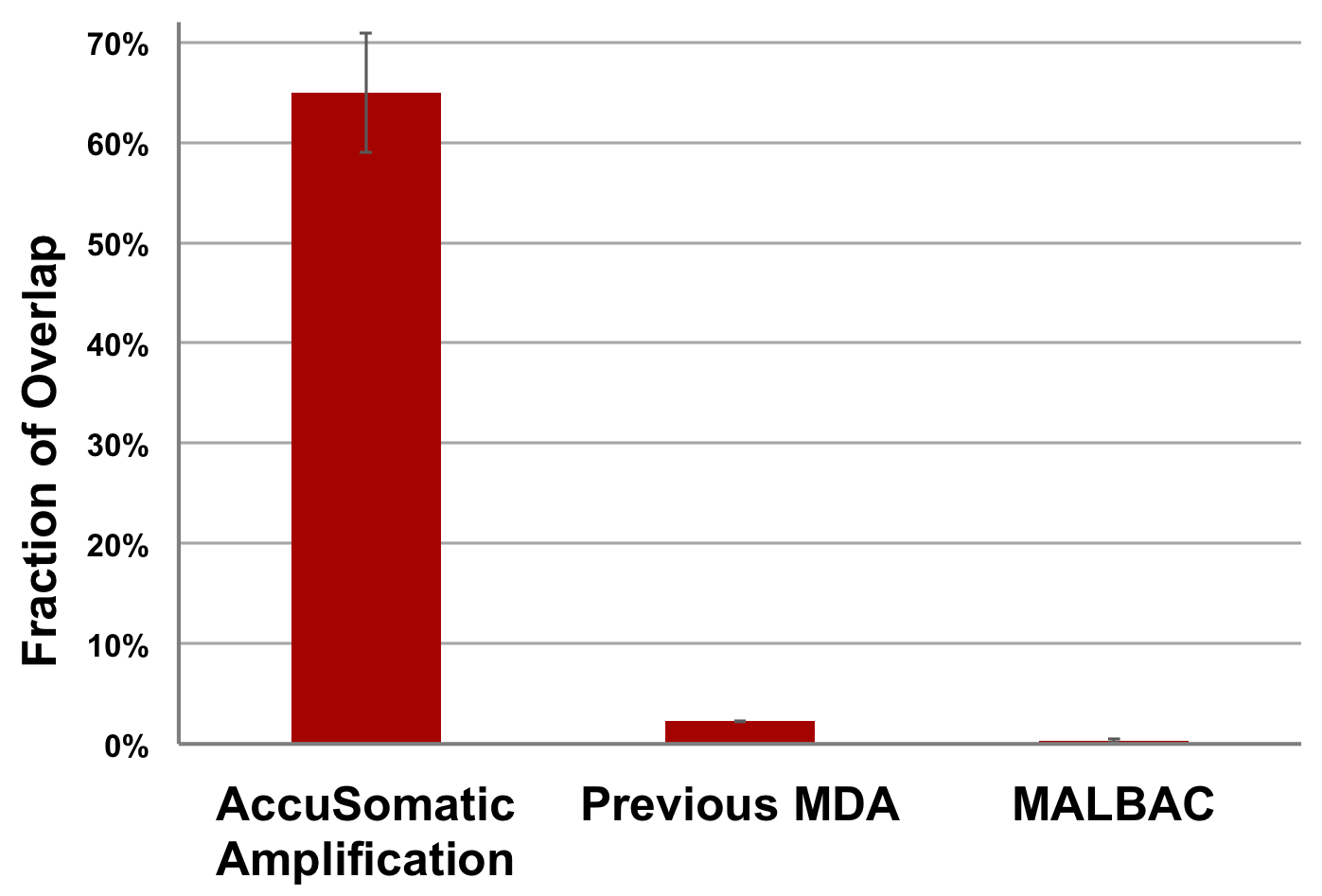
Figure 2. AccuSomatic Amplification generates correct somatic SNV calls while prior methods generate almost entirely false-positive results.
Significant overlaps of somatic SNVs are expected among a group of kindred single cells because they inherit many of the same somatic mutations from their common parental cell. AccuSomatic Amplification is the only method that gives the correct result (65% overlap). Methods such as MALBAC and commercial MDA kits are so overwhelmed by false positives that the true mutations only make up a negligible fraction (0.3% and 2% overlap, respectively) among the artifacts. All conventional methods suffer from the same problem [1].
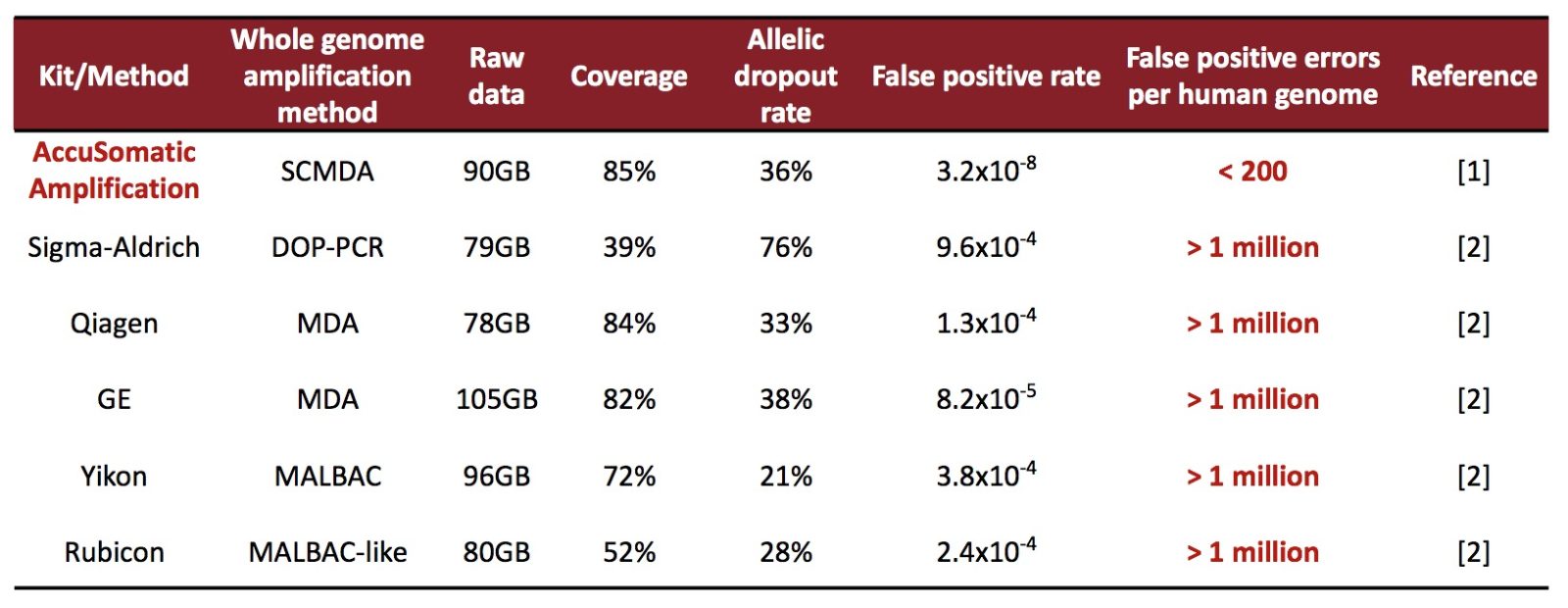
Table. AccuSomatic Amplification significantly outperforms commercial kits in mutation detection accuracy.
False positive rate (FPR) = FP/N. FP is number of false positives; N is number of negatives.
The number of false positive errors per human genome is FPR times the diploid size of the human genome.
[1] Dong X et al. Nat Methods. 2017 May;14(5):491-493
[2] Huang L et al. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2015;16:79-102
The AccuSomatic Amplification Service by SingulOmics®
AccuSomatic Amplification is an integrated experimental and computational system for discovering true somatic SNVs unique to a single cell. SingulOmics provides an end-to-end solution from isolated single cells to true SNV discovery (Figure 3). Amplified DNA products can serve as materials for whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing, targeted sequencing, and Sanger sequencing. We also provide downstream variant calling of SNVs, small insertions and deletions as well as copy number variations using the optimized bioinformatics pipeline for single cell analyses.
Figure. 3 AccuSomatic Amplification Service Workflow.
Sample Requirements
Samples can be submitted as single cells (nuclei) or as frozen cells in cell suspensions.
(1) Single cells (nuclei): Please click here to access instructions on how to collect single cells.
(2) Frozen cells of single population in cell suspensions: We provide single cell isolation service using CellRaftTM. Please click here for sample requirements.
If you have additional requirements for single cell isolation (e.g. single cell population from blood or tissues), please contact us.
Turnaround Time
10 working days for whole genome amplification
Publications
- Dong X et al. 2017. Accurate identification of somatic single nucleotide variation from whole genome amplified single cells. Nature Methods 14: 491-493 doi:10.1038/nmeth.4227
- Li et al. 2023. Single-neuron whole genome sequencing identifies increased somatic mutation burden in Alzheimer's disease related genes. Neurobiology of Aging 123:222-232. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2022.12.002
- Bloom J et al. 2020. Sexually dimorphic DNA damage responses and mutation avoidance in the mouse germline. Genes & Development 1;34(23-24):1637-1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.341602.120
- Sarangi V et al. 2020. SCELLECTOR: ranking amplification bias in single cells using shallow sequencing. BMC Bioinformatics 21(521) doi 10.1186/s12859-020-03858-y
- Zhang L et al. 2019. Single-cell whole-genome sequencing reveals the functional landscape of somatic mutations in B lymphocytes across the human lifespan. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(18):9014-9019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902510116
- Milholland B et al. 2017. Differences between germline and somatic mutation rates in humans and mice. Nature Communications 8:15183. doi:10.1038/ncomms15183
- Gundry M et al. 2012. Direct, genome-wide assessment of DNA mutations in single cells. Nucleic Acids Research 40(5):2032-40
Next Steps...
Contact us to learn more or get a price quote.
